2/3 of world production is actually used mixed in the proportions occuring naturally in the ore 1. Cerium & Europium may be extracted Chemically:- Oxidize only Ce to M4+ by HClO or KMnO4, then precipitate as CeO2 or Ce(IO3)4
- On action of Zn/Hg only Eu forms a stable M2+ that doesn't reduce H2O, then isolate by precipitation as EuSO4
2. Separation by Fractionation:Small Scale methods used originally:• Fractional Crystallization of e.g. Ln(NO3)3.2NH4NO3.4H2O or Ln(BrO3)3 • Fractional Thermal Decomposition of e.g. Ln(NO3)3 Current Small Scale Lab. Separation:• Ion-Exchange Displacement Column - Ln3+(aq) are strongly adsorbed by a cation-exchange resin
- add an eluant ligand
typically chelating ligandse.g. EDTA  , or 2-hydroxy-EDTA , or 2-hydroxy-EDTAe.g. HIB{[[alpha]]-hydroxyisobutyric acid}  - Ligand binds most strongly to smallest ion
e.g. the binding constants of the Ln(EDTA) complexes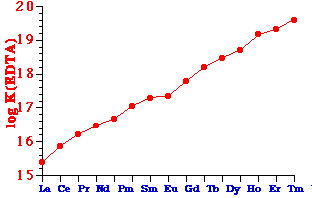
- Elution order is Lu Æ La
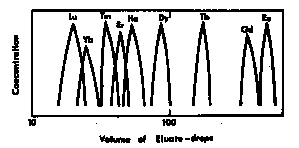 - The process of separation is indicated graphically
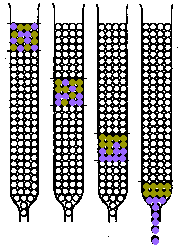 greater detail on these columns may be found in:-- Greenwood & Earnshaw, p. 1427-1428
- Open University S304 Unit 27, p. 20-22
Current Large Scale Industrial Separation:Solvent Extraction - Ln3+(aq) is extracted in a continuous counter-current process into a non-polar organic liquid (e.g. kerosene)
- the kerosene contains ca. 10% of
- bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphinic acid (DEHPA)
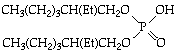
or - tri-n-butylphosphine oxide (TBPO) (nBu3O)3PO
- solubility of Ln3+ in organic solvent increases with its RAM
- separation factor for adjacent rare earths = 2.5
- automatic multistep, counter-current conditions Æ 99.9% purity Ln
  Bibliography [textbook & online resources] Bibliography [textbook & online resources] |

