Solubility Hydrated Lanthanide IonsCoordination Compounds- Classic bidentate complexes formed as Ln(L-L)3L' (L' = H2O, py, etc...) or Ln(L-L)4
- dehydrate Ln(L-L)3(H2O) in vacuo -> Ln(L-L)3 now coordinatively unsaturated!
- Ln(L-L)3 with bulky R
e.g. Eu(facam)3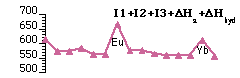 - "Anti-knock" activity as petroleum additives
- Macrocyclic Ligands
Crown Ethers - Complexes with
- uncharged monodentate ligands
- ligands with donor atoms other than O
MUST be prepared in the absence of H2O- e.g. Ln(en)43+ (8-coordinate) from polar organic solvents (e.g. acetone)
- (18-crown-6) complexes dissociate instantly in water!
Solution Chemistry of Other Lanthanide Oxidation StatesLn(IV) Cerium is the only Ln4+ with significant aqueous or coordination chemistry E° (Ce4+(aq)/Ce3+(aq)) = 1.72 V (others est. „ 2.9 V) Ln(II) Significant solution chemistry of Ln2+ is essentially confined to SmII, EuII, YbII Preparation: - electrolytic reduction of Ln3+(aq)
- Eu2+ (the most stable LnII) is prepared by reduction of Ln3+(aq) with Zn/Hg
Properties   Bibliography [textbook & online resources] Bibliography [textbook & online resources] |

